The race to develop artificial intelligence is transforming the global landscape, driving a monumental surge in demand for computing power unlike anything the industry has seen before. At the heart of this transformation are specialized computer chips known as GPUs (graphics processing units), originally designed for video games. Now, tech companies are packing these chips into massive data centers, sparking a construction boom and raising critical questions about energy consumption and environmental impact.

GPs are ideal for running the complex calculations that power AI systems, especially the neural networks at the core of chatbots and other leading AI technologies. This has led to a surge in demand, forcing tech companies to cram as many GPUs as possible into facilities known as data centers.
This new kind of supercomputer involves wiring together tens of thousands of chips, demanding building-sized facilities to house them. OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT, plans to construct roughly five facilities that would collectively consume more electricity than the roughly three million households in Massachusetts. This massive power consumption comes at a significant cost.

Data centers are popping up across the United States and around the globe. Tech giants are aggressively hunting for the power to run them and the water needed to cool the chips, which are prone to overheating.
This shift in computing marks one of the most fundamental changes since the early days of the World Wide Web. Companies are rebuilding their infrastructure from the ground up, from the fundamental components to the very architecture of their facilities, to accommodate this intense demand for AI.
Previously, data centers handled online traffic for services like search engines, email, and e-commerce. However, they are now being reimagined to handle the enormous requirements of AI. In 2006, Google opened its first data center in The Dalles, Ore., at a cost of roughly $600 million. OpenAI and its partners, however, announced a plan to spend approximately $100 billion on new data centers, beginning with one in Texas. They intend to invest an additional $400 billion into similar facilities across the United States.
This radical transformation is impacting not only technology but also finance, energy markets, and local communities. Private equity firms are pouring money into data center companies, and electricians are moving to areas where these facilities are being built. Simultaneously, some local communities voice concerns about the potential negative consequences of these large-scale projects.
Currently, tech companies are looking for more computing power and more electricity than the world can readily provide. The industry is responding aggressively; OpenAI is aiming to raise hundreds of billions of dollars to construct computer chip factories. Google and Amazon have made deals to introduce a new generation of nuclear reactors, and they are eager to move quickly.

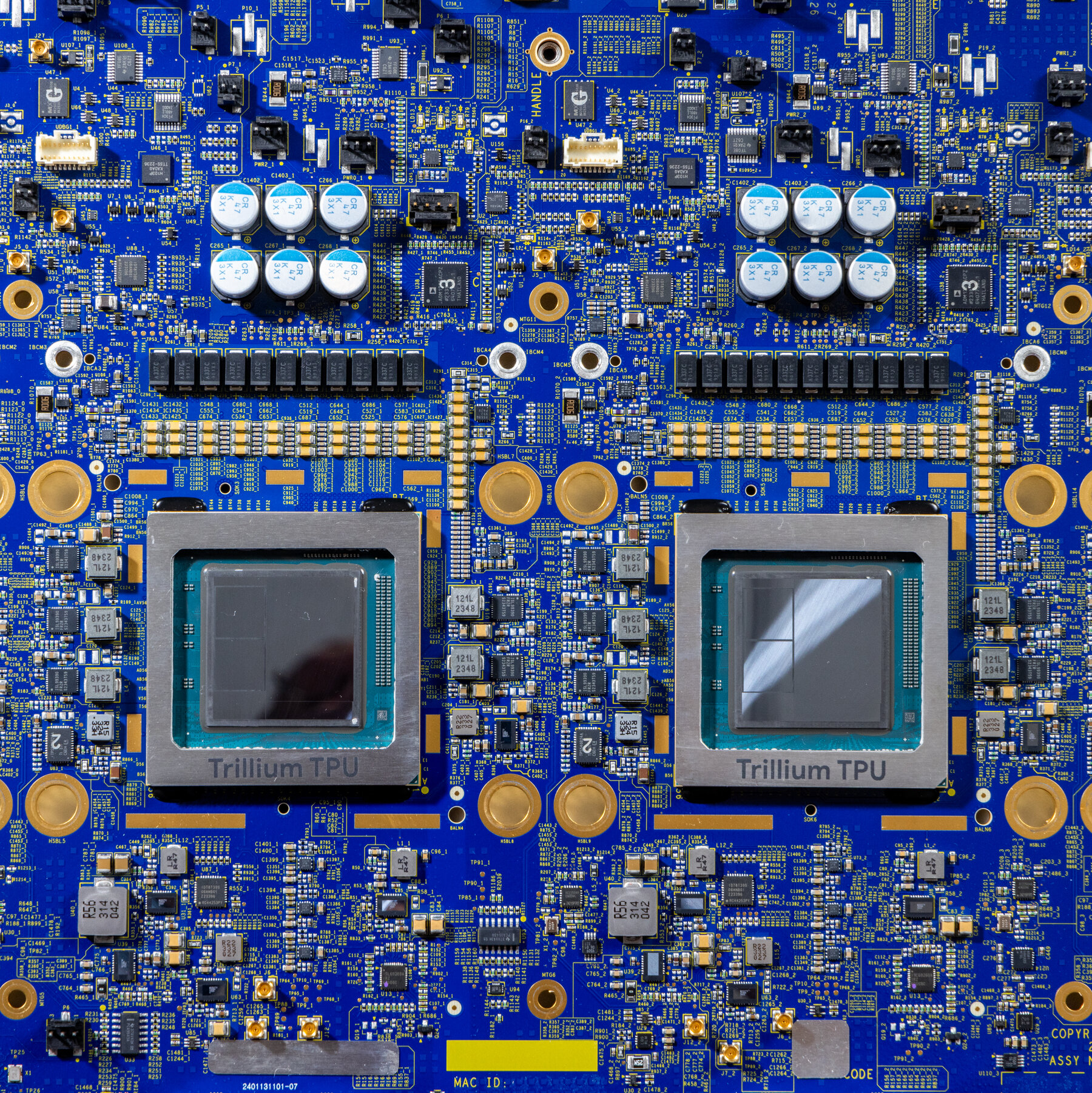
At the core of this computing revolution lies the specialized chip known as the GPU. Nvidia, a pioneering Silicon Valley chipmaker, originally designed these chips to render graphics for video games. GPUs, however, excel at the mathematical functions that drive neural networks. Because GPUs can process many calculations at once, allowing AI models to analyze more data, they are the perfect solution for the demands of today’s AI.
In previous generations of computing, CPUs, or central processing units, performed many functions, but they processed data in a sequential manner. GPUs use parallel processing, enabling AI to analyze massive datasets much more efficiently.
These are very different from chips used to just serve up a web page. They run millions of calculations as a way for machines to ‘think’ about a problem.
– Vipul Ved Prakash, the chief executive of Together AI.
Companies are deploying increasing numbers of GPUs to construct more powerful AI technologies. The change is so intense that the industry is rethinking the way its chips operate, and the facilities that house them.
Meta, for example, built its Eagle Mountain data center in Utah. To further accelerate the performance of AI systems, companies seek to minimize the distance data must travel among the chips.

In 2021, Meta had two data centers near Salt Lake City and was constructing three more to power social media apps. After the release of ChatGPT, Meta re-evaluated its AI strategy and had to install thousands of GPUs into a data center to perform the calculations needed to build a single neural network. Meta subsequently started construction on its sixth and seventh Utah data centers. In these facilities, each about 700,000 square feet, technicians load racks with hardware to train AI, inserting machines packed with GPUs, which can cost tens of thousands of dollars each.
AI systems require prodigious amounts of power, which has led to a race to build new data centers. Cirrascale leased a conventional 139,000-square-foot data center in Austin, Texas, that previously used about 5 megawatts of electricity, enough for roughly 3,600 homes. By equipping the facility with GPUs instead of conventional CPUs, the same amount of power now runs only eight to 10 rows of computers. OpenAI, meanwhile, is aiming to build five data centers that will collectively consume more electricity than approximately three million households.
Data centers consumed about 4.4 percent of total electricity in the United States in 2023, or more than twice as much power as cryptocurrency mining facilities consume. According to a December report by the Department of Energy, that figure could triple by 2028.

Time is the currency in the industry right now. I don’t see this slowing down in the next few years.
– Arman Shehabi, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
The demand for power has created a bottleneck. Some AI companies are now considering nuclear power to address their needs. Microsoft is restarting the Three Mile Island nuclear plant in Pennsylvania, while Elon Musk’s xAI is installing gas turbines for a new data center in Memphis.
Because AI systems generate considerable heat, cooling is a challenge for data centers. If a rack isn’t adequately cooled, the machines, and the entire data center, can be at risk of fire.
To solve this problem, Google has developed a system that pumps cold water directly through the racks of computers. The water absorbs heat and keeps the chips from malfunctioning. In a traditional data center, cold air is pumped up from vents, and heated air exits the servers and is pulled into an air-conditioning unit, circulating in a loop. For AI data centers, cool water circulates through pipes at the front of the rack, absorbing heat directly and allowing for greater cooling. The heated water then flows through air-conditioning units.
Large-scale water use can strain local supplies, requiring companies to find alternate methods, like using chillers, but this process also consumes significant electrical power.
Google broke ground on 11 data centers last year. Meta announced its facility in Louisiana would be large enough to encompass a significant portion of New York’s Central Park. Mark Zuckerberg, Meta’s CEO, highlighted in a Facebook post, “This will be a defining year for AI.”