AI Tool Creates Detailed 3D Map of Mouse Brain Metabolism, Promising Advances in Alzheimer’s Research
Researchers at the University of Florida have made a significant breakthrough in brain research. They’ve created a powerful new computational and artificial intelligence tool capable of generating a high-resolution 3D map of the brain in mice. According to the researchers, this tool will allow scientists to zoom in and out, like a Google Earth map, and examine the full set of molecules that power brain functions. This advancement brings scientists one step closer to understanding the role of metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders, with the potential to unlock new avenues for targeted treatments.
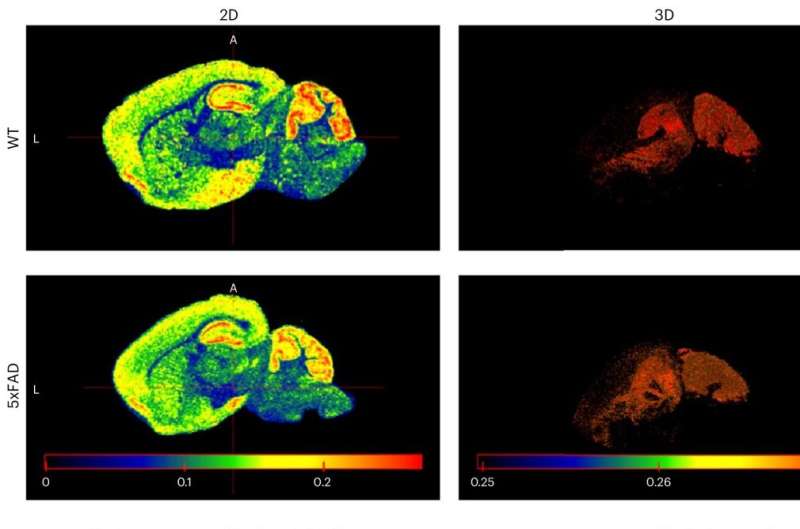
The findings, published in the journal Nature Metabolism, detail the creation of the MetaVision3D tool, developed using UF’s HiPerGator supercomputer. As a proof of concept, the team generated an interactive 3D atlas of the brain in both normal mice and mouse models of Alzheimer’s and Pompe disease, a rare genetic disorder. The researchers have made their database and web server publicly accessible to support the growing field of scientists investigating the connections between metabolism and mental health.

Pathway enrichment analysis of neuronal layers of the hippocampus in WT and 5xFAD mouse brains. Credit: Nature Metabolism (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s42255-025-01242-9
“Using our methodology, we can map thousands of molecules in the brain and precisely where they are located inside each brain region. It is unprecedented,” said Ramon Sun, Ph.D., director of the Center for Advanced Spatial Biomolecule Research and associate director for innovation of UF’s McKnight Brain Institute.
The 3D reconstruction offers a level of detail not previously attainable with conventional 2D maps. This allows researchers to explore nuances of cellular metabolism – processes influenced by diet, exercise, and genetics – as well as gain insights into the mechanisms of diseases. “On Google Earth, I can zoom in on a city and see what a house looks like, what the street looks like, what cars are there. That’s the level of resolution we provided for the mouse brain in this three-dimensional space, and how they change during diseases,” Sun explained. Moreover, according to Sun, this new tool can help researchers explore and examine molecules that influence functions like thinking, memory, and overall brain health, including those involved in neurodegenerative diseases.

MetaVision3D, a computer vision pipeline for the generation of spatial metabolism in 3D. Computational framework for MetaVision3D for the generation of spatial metabolome of mouse hemibrain in 3D. Created with BioRender.com. Credit: Nature Metabolism (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s42255-025-01242-9
To achieve the detailed 3D representation, the team scanned 79 brain sections, each a thin layer. They used a high-tech imaging machine to identify and count molecules such as fats and carbohydrates, vital nutrients for brain function. Xin Ma, a first author of the paper and doctoral student in biostatistics, noted that “Then we used AI to align those images and stack them together to reconstruct the whole brain metabolome.” The metabolome constitutes the collection of thousands of molecules that provide energy for the brain to function.
As the next step, researchers worked with Sara Burke, Ph.D., director of UF’s Center for Cognitive Aging and Memory Clinical Translational Research, to map the anatomy to correlate with the molecules. They used mathematical methods to verify an accuracy of 95 to 99% of their tool. Looking ahead, researchers plan to integrate this advanced map-making tool with established MRI imaging and genetic analyses to develop treatments which address precise targets within the brain. Chen, a co-corresponding author of the paper and an associate professor in the UF College of Public Health and Health Professions’ Department of Biostatistics, said, “For disease prevention and treatment, we have opened a new angle for biologists to study.”
More information: Xin Ma et al, AI-driven framework to map the brain metabolome in three dimensions, Nature Metabolism (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s42255-025-01242-9
Journal information: Nature Metabolism
Provided by: University of Florida