Artificial intelligence is increasingly being integrated into our daily lives while driving significant breakthroughs in scientific research. Recent studies published in Nature and Nature Machine Intelligence demonstrate how generative AI foundation models can dramatically accelerate the discovery of new materials and enhance medical care through faster analysis of radiology results. These advancements are the result of collaborative efforts between Microsoft, academic institutions, and the private sector.
Accelerating Materials Discovery with MatterGen
The development of new materials has been a crucial factor in human progress, from the steel used in modern construction to the silicon chips powering today’s smartphones. However, this process has traditionally been time-consuming and costly, involving the screening of millions of potential materials over years. MatterGen, a new generative AI model developed by Microsoft Research, offers a revolutionary approach. By specifying desired properties, researchers can generate new materials tailored to those characteristics, significantly streamlining the discovery process. Initial experiments have shown promising results, with synthesized materials exhibiting properties within 20% of the targeted specifications.

The potential impact of MatterGen is vast, with applications in fields such as electronics, energy storage, and biomedical engineering. For instance, developing more efficient battery materials could lead to more sustainable energy storage solutions, while advancements in superconductors might revolutionize medical imaging or quantum computing. “From an industrial perspective, the potential here is enormous,” notes Tian Xie, principal research manager at AI for Science Cambridge. “If we can use generative AI to make materials design more efficient, it could accelerate progress in industries like energy, healthcare, and beyond.”
Enhancing Radiology with RAD-DINO
In a separate breakthrough, Microsoft Research and Mayo Clinic are collaborating on RAD-DINO, a multimodal foundation model that integrates text and images for radiology applications. This technology aims to provide doctors with more comprehensive medical data faster, potentially speeding up diagnoses and improving patient care. By identifying anatomical matches between chest X-rays of different subjects, RAD-DINO can help personalize patient care and enhance diagnostic accuracy. Initial efforts focus on developing a model that automatically generates reports, evaluates the placement of tubes and lines through chest X-rays, and detects changes from prior images.
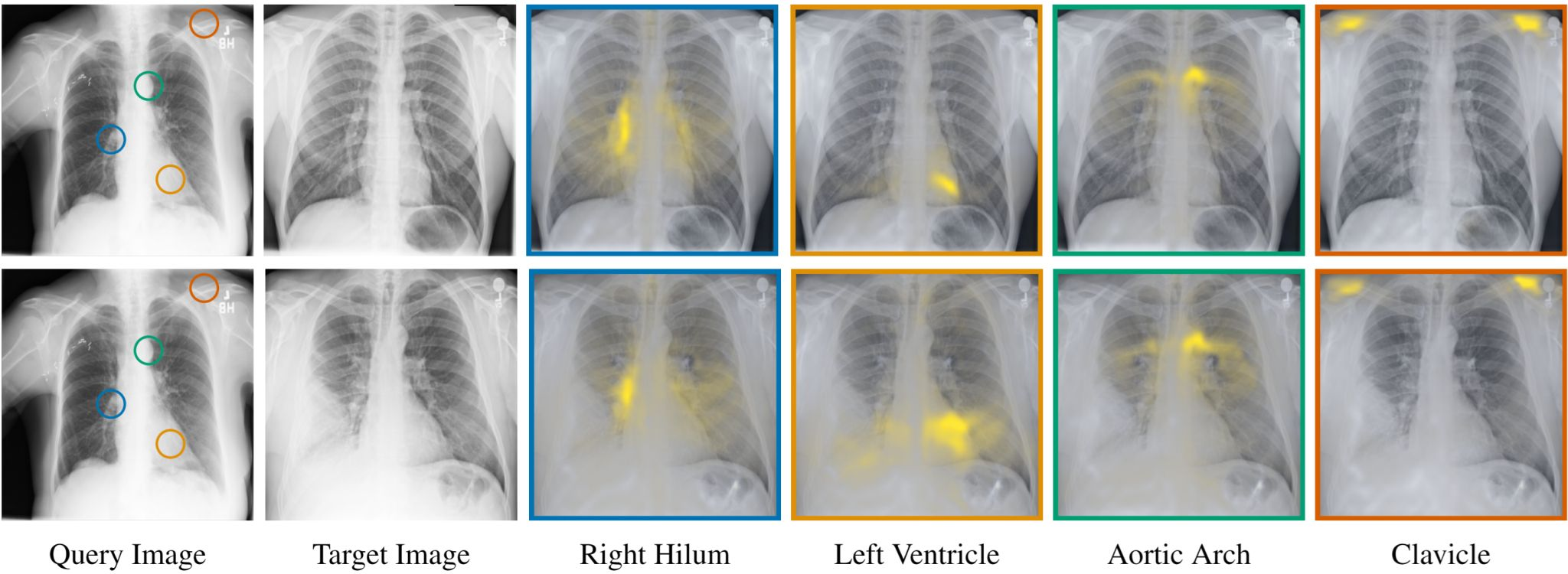
“I am excited to share our collaboration with Mayo Clinic… to tackle one of the most pressing challenges in healthcare: delivering faster and more precise medicine,” says Javier Alvarez Valle, senior director of Multimodal AI at Microsoft Health Futures UK. The integration of generative AI into clinical workflows has the potential to transform how clinicians work and care for patients by providing more efficient and comprehensive analyses of medical images.

