Top Tech Trends Shaping Businesses in 2024
The McKinsey Technology Council has released its latest analysis, identifying the most critical technology trends for businesses in 2024. The report highlights the adoption, development, and industry-wide impacts of these advanced technologies. Despite a challenging economic climate in 2023, continued investment in these frontier technologies points to substantial growth in enterprise adoption.
Generative AI (gen AI) has emerged as a standout trend since 2022, experiencing a considerable surge in interest and investment. This surge is unlocking innovative possibilities across interconnected fields, including robotics and immersive reality. While macroeconomic factors, such as elevated interest rates, have influenced equity capital investments and hiring trends, underlying indicators remain positive. Optimism, a strong focus on innovation, and the sustained need for long-term talent all contribute to a positive trajectory in the fifteen technology trends analyzed.
What’s New in This Year’s Analysis
This year’s analysis reflects shifts in the technological landscape with two key changes: the integration of digital trust and cybersecurity (incorporating what was previously referred to as Web3 and trust architectures) and the inclusion of the future of robotics.
The report also highlights the synergy between robotics and AI, which is paving the way for groundbreaking innovations and shifts across the economic and workforce landscapes. Additionally, the council deployed a survey to measure adoption levels across trends. These findings are detailed in the McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook, which aims to help executives plan ahead by providing insights into potential use cases, value sources, adoption drivers, and the critical skills needed to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Key Findings
Two trends stood out in 2023: gen AI and electrification and renewables. Gen AI saw a nearly 700 percent increase in Google searches between 2022 and 2023, alongside notable jumps in job postings and investments. The pace of innovation has been remarkable.
Consider the advancements in large language models (LLMs), with the size of prompts they can process – known as “context windows” – increasing significantly. This expansion allows for the incorporation of vast amounts of data, like approximately 20 novels, into a model prompt. The types of data that gen AI can process have also expanded to include, notably, video, images, audio, and text. This has fueled investments and innovations in more powerful computing systems.
Large foundation models that power generative AI, such as LLMs, are now being integrated into various enterprise software tools and used for powering customer-facing chatbots, generating ad campaigns, and accelerating drug discovery. This expansion is expected to continue, pushing boundaries on the capabilities of AI.
Senior leaders’ increased awareness of gen AI innovation has increased interest and investment in other AI technologies, particularly robotics, which is a new trend in this year’s analysis. Advancements in AI are ushering in an era of more capable robots, spurring innovation and wider deployment.
Research Methodology
To assess the development of each technology trend, the McKinsey team gathered data on five key activity measures: search engine queries, news publications, patents, research publications, and investment. For each measure, the team used a defined set of data sources to identify occurrences of keywords associated with each trend, screening these occurrences for valid mentions of activity. Their innovation score combined the patents and research scores, and the interest score combined the news and search scores.
The data sources used by the team include:
- Patents: Data on patent filings are sourced from Google Patents.
- Research: Data on research publications are sourced from Lens.
- News: Data on news publications are sourced from Factiva.
- Searches: Data on search engine queries are sourced from Google Trends.
- Investment: Data on capital raises (venture capital, corporate and strategic M&A, private equity, and public investments) are sourced from PitchBook.
- Talent Demand: Number of job postings is sourced from McKinsey’s proprietary Organizational Data Platform.
In addition, the selection and definition of the trends were updated from previous reports to reflect the evolution of technology trends. Finally, survey data were used to calculate enterprise-wide adoption scores for each trend. The survey included approximately 1,000 respondents from 50 countries with senior-level professionals knowledgeable in technology.
Adoption and Investment Trends
The other trend that defied economic headwinds was electrification and renewables, which earned the highest investment and interest scores. Job postings in this sector also saw a moderate increase. Despite investment and hiring declines in many trends during 2023, the long-term outlook remains positive. This optimism is supported by continued long-term growth in job postings for the analyzed trends. Moreover, enterprises continue to innovate and show increased interest in harnessing the power of these technologies, particularly for future growth.
In 2023, technology equity investments declined by 30 to 40 percent to approximately $570 billion due to rising financing costs. This prompted investors to favor technologies with strong revenue and margin potential. This approach is in line with the strategic perspectives of leading companies. They recognize that full adoption and scaling of cutting-edge technologies is a long-term endeavor.
While many technologies maintained cautious investment profiles over the past year, gen AI saw a sevenfold increase in investments, driven by advancements in text, image, and video generation. Despite an overall downturn in private equity investment, innovation has accelerated in the three trends that form part of the “AI revolution” group: gen AI, applied AI, and industrializing machine learning.

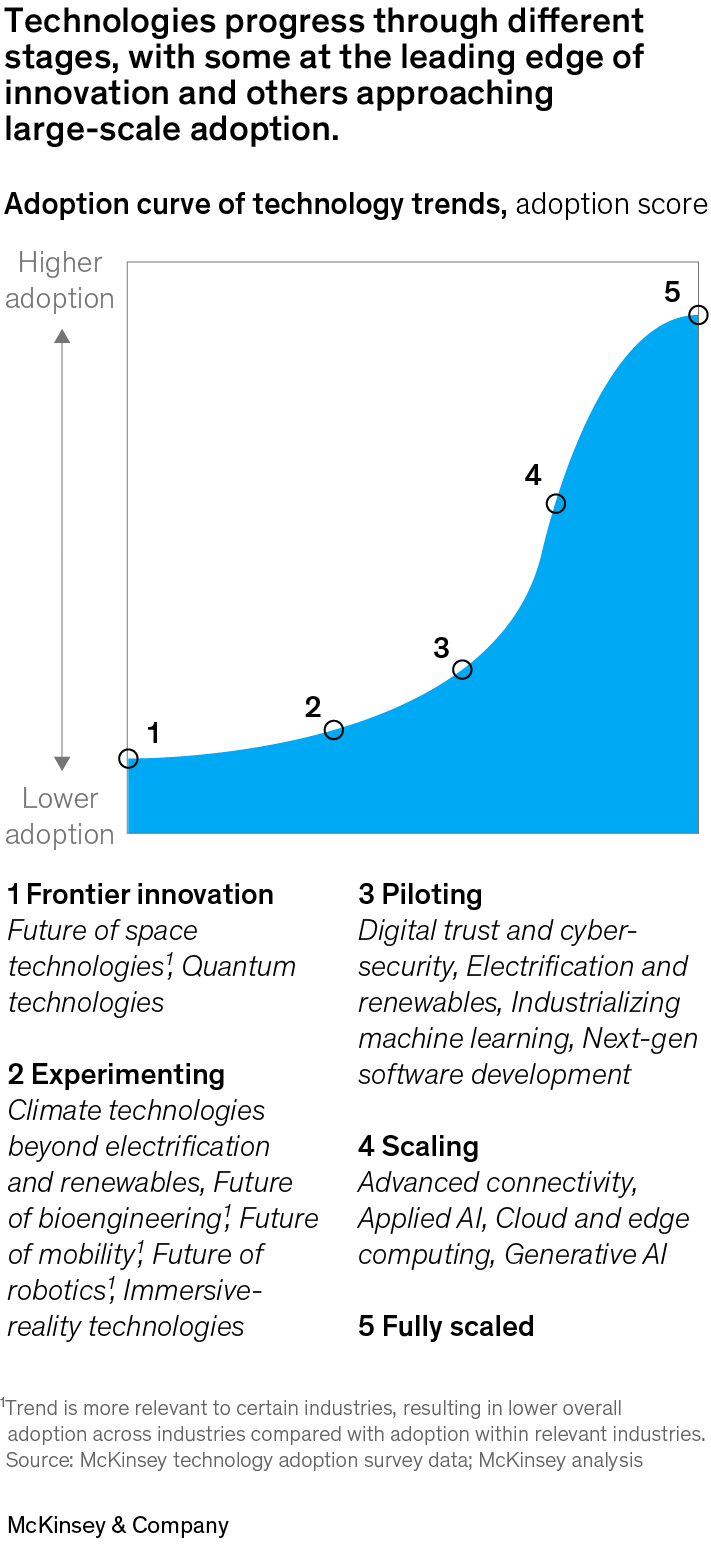
The adoption curve of technology trends, scored from 1 to 5, where 1 represents frontier innovation and 5 represents fully scaled.
Applied AI and industrializing machine learning, fueled by the growing interest in gen AI, have seen significant innovation. Electrification and renewable-energy technologies maintain high interest, driven by a surge in global renewable capacity, their vital role in decarbonization efforts, and the heightened need for energy security.
The talent environment mirrored investment trends in 2023. The technology sector experienced layoffs, particularly among large companies, with tech-trend-related job postings declining. Despite these reductions, trends with robust investment and innovation, like gen AI, both maintained and increased job postings, reflecting a strong demand for specialized skills. Electrification and renewables also saw positive job growth, partially due to public sector support for infrastructure. The analysis also highlighted a skills gap across the 15 tech trends.

A segmented bar graph showing the adoption levels of tech trends.
The scaling of technology adoption also depends on a supportive external ecosystem. User trust, business model viability, regulatory environments, and talent availability are all crucial. Since these ecosystem factors vary significantly by geography and industry, different adoption scenarios are playing out.
Executives should consider both internal capacities and external ecosystem conditions to ensure successful technology integration. They should monitor these factors to make informed investment decisions and navigate uncertainties on the path to full technology adoption. Leaders who adopt a long-term view—building talent, testing and learning for impact, and reimagining their businesses for future success—are well-positioned to thrive in the rapidly evolving technology landscape.
Lareina Yee, Michael Chui, Roger Roberts, and Mena Issler authored the report.