AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Medical Images
February 27, 2025
According to a recent study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, Cornell’s Ithaca campus, and Cornell Tech, a new AI-based system can accurately detect changes and predict outcomes from images taken over time. The system, called LILAC (Learning-based Inference of Longitudinal imAge Changes), demonstrates potential across a wide range of medical and scientific applications due to its sensitivity and flexibility.
LILAC employs a machine learning approach to analyze longitudinal image series. These image series, which capture changes over time, can be used to study a wide range of events, from developing IVF embryos to healing tissue after wounds and aging brains.
“This new tool will allow us to detect and quantify clinically relevant changes over time in ways that weren’t possible before, and its flexibility means that it can be applied off-the-shelf to virtually any longitudinal imaging dataset,” said Dr. Mert Sabuncu, senior author of the study and vice chair of research and professor at Weill Cornell Medicine and Cornell University.

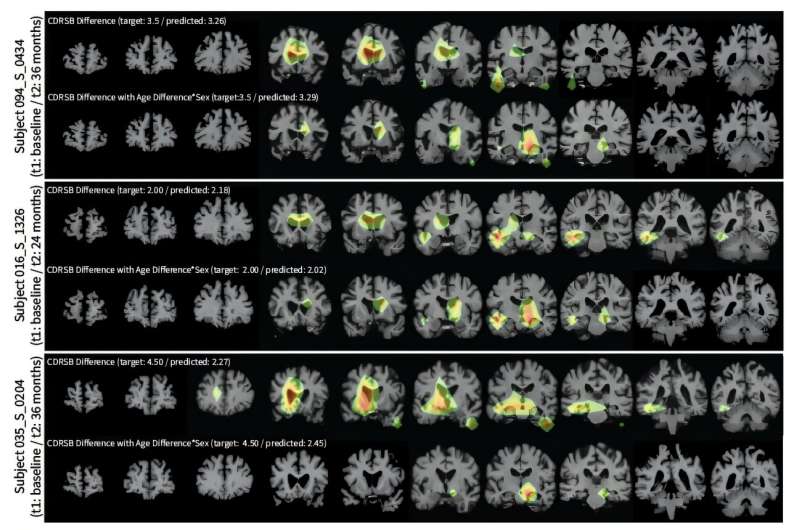
This image presents heatmaps highlighting the areas LILAC focuses on when making predictions. The top section illustrates LILAC’s prediction of changes in the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale Sum of Boxes, a dementia scoring system, while the bottom section accounts for age and sex as additional factors. The differences in the highlighted regions suggest that the model relies on different parts of the image depending on whether these factors are considered. Credit: Dr. Heejong Kim
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on February 20, provides a comprehensive overview of LILAC’s capabilities. Traditional methods for analyzing longitudinal image datasets often require extensive customization and pre-processing. LILAC, however, is designed to work more flexibly, automatically performing corrections and finding relevant changes. Dr. Heejong Kim, the study’s first author and an instructor of artificial intelligence at Weill Cornell Medicine, noted the system’s adaptability.
“This enables LILAC to be useful not just across different imaging contexts but also in situations where you aren’t sure what kind of change to expect,” Dr. Kim said.

Schematic overview of Learning-based Inference of Longitudinal imAge Changes (LILAC), a learning-based method for inferring longitudinal image changes. (Top) Architecture design of LILAC. (Middle) Two major prediction tasks are to predict temporal order (LILAC-o) and change of specific value. Examples of predicting specific changes include time intervals (LILAC-t) and cognitive scores with additional variables (LILAC-s). The predictions from each task are utilized for quantitative analysis, while the localization of prediction contributors enables qualitative analysis. (Bottom) Real-world applications using medical imaging datasets, with example image pairs demonstrating input for LILAC-based analysis. Credit: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2025). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2411492122
To demonstrate LILAC’s capabilities, the researchers trained the system on various image sets. In one demonstration, LILAC analyzed sequences of microscope images detailing in-vitro-fertilized embryos. The system then determined, with approximately 99% accuracy, the correct temporal order of the images. LILAC also accurately analyzed data from healing tissue, identifying differences in healing rates. The system correctly predicted time intervals between MRI images of healthy older adults’ brains. It likewise predicted cognitive scores from MRIs of patients with mild cognitive impairment with significantly less error compared to other baseline methods. These results highlight LILAC’s potential to improve clinical and scientific progress.
“We expect this tool to be useful especially in cases where we lack knowledge about the process being studied, and where there is a lot of variability across individuals,” Dr. Sabuncu indicated.
The researchers are now planning to use LILAC in a real-world setting to predict the effectiveness of treatments for prostate cancer patients using MRI scans.
More information: Kim, H., et al. (2025). Learning-based inference of longitudinal image changes: Applications in embryo development, wound healing, and aging brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2411492122