Blockchain Platforms for Businesses: An Enterprise Guide
Interest in blockchain technology is surging as a way to streamline supply chains, improve traceability, and simplify financial transactions. Modern blockchain platforms have evolved to overcome the limitations of early cryptocurrency platforms like Bitcoin, offering tangible benefits for business applications.
Adoption and Use Cases
Enterprises are increasingly adopting these platforms, especially for applications requiring multiparty cooperation and data exchange. Suseel Menon, practice director at Everest Group, cites supply chain tracking, trade finance, digital assets, and identity management as areas moving beyond the pilot stage. There’s also activity in using blockchain for certain functions of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), such as vendor and supply chain management.
Furthermore, the rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is driving demand for blockchain platforms, enabling new business models that challenge traditional banking, finance, and supply chain finance.
Top Blockchain Platforms
Here are eight prominent blockchain platforms that businesses should consider:
1. Ethereum
Introduced in 2013, Ethereum is one of the oldest and most established blockchain platforms. It provides a decentralized blockchain and robust support for smart contracts, self-executing programs considered a potential “killer app” for blockchain. Alongside its role as a platform for enterprise applications, Ethereum has its own cryptocurrency, ether.

Suseel Menon
The Ethereum platform is widely adopted by developers building decentralized applications (dApps). It supports numerous platforms and exchanges for non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which are digital assets that can be exchanged on a blockchain. Ethereum boasts a mature ecosystem of tools for writing smart contracts using the Solidity programming environment.
While alternative blockchain networks may offer faster transaction processing at a lower cost, the Ethereum community migrated from a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to Proof of Stake (PoS) in 2022, which is more energy-efficient. The Ethereum Foundation estimates this reduces energy use by 99.95% compared to PoW. The Enterprise Ethereum Alliance, with around 50 members including Accenture, JPMorgan Chase, and Microsoft, actively supports the Ethereum developer community.
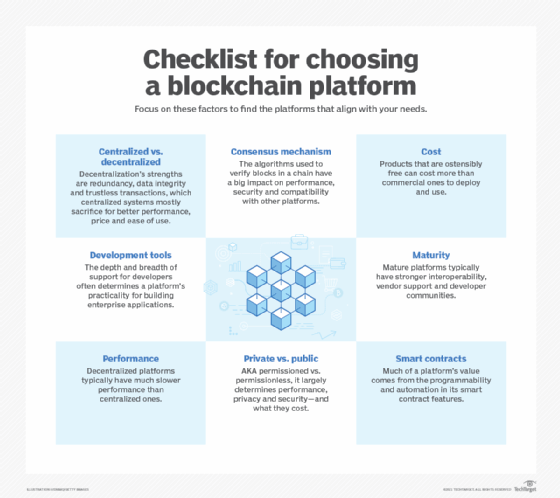
Choosing a blockchain platform involves considering factors like performance and cost.
2. IBM Blockchain
IBM Blockchain is a private, decentralized network ideal for integrating with enterprise cloud and legacy technologies. IBM claims significant progress in financial services, banking, and supply chain applications. Examples include IBM Food Trust, a SaaS network connecting the supply chain to ensure food safety and traceability, and the Blockchain Community Initiative in Thailand, which supports services like payment obligations and enterprise auctions for Thai banks.
IBM Blockchain Transparent Supply, another platform application, improves traceability in supply chain management. It offers features for quality assurance, forecasting improvements, and tools to reduce dispute resolution costs, product recalls, and document sharing. It also provides tools to help manufacturing, retail, pharmaceutical, and consumer goods companies launch blockchain projects.
IBM has also invested in a user-friendly interface to simplify tasks such as setting up, testing, and deploying smart contracts.
3. Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric is a set of tools for creating blockchain applications, spearheaded by the Linux Foundation. It’s designed for enterprise distributed ledger use, offering a rich ecosystem of modular components that work well in closed deployments, thus enhancing security and speed. It utilizes an open smart contract model supporting various data models. Data privacy is improved through channel isolation or need-to-know private data collections. Hyperledger Fabric also delivers high-speed transactions with low finality latency, and it is supported by leading cloud providers.

Chris Georgen
An active community continues to enhance Hyperledger Fabric with features related to consensus algorithms, privacy options, and operational improvements. Version 3.0, released in September 2024, added support for Byzantine fault tolerance, a consensus mechanism that functions even with some malfunctioning nodes. Chris Georgen, board member and advisor at Apparatus, recommends that enterprises evaluate blockchain platforms based on:
- Open vs. Closed: Public (open) blockchains are easier to set up but slower. Many codebases can be adapted for both.
- Consensus Mechanism: Examples include PoW, PoS, and Byzantine fault tolerance. PoS and Byzantine fault tolerance are newer and less proven than POW but faster and more energy-efficient.
- Ledger Technology: This refers to how transactions are recorded. Popular approaches include the account model and UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model.
- Smart Contract Functions: These capture business logic on the blockchain, with popular programming languages including Ethereum’s Solidity.
4. R3 Corda
R3 Corda, sometimes considered an alternative distributed ledger, uses a unique consensus mechanism where transactions are cryptographically linked, but not batched into blocks. This allows all transactions to be processed in real-time, which can improve performance. Corda has a significant following in the financial industry due to its attractive approach for financial transactions and smart contracts with strong security. Key proponents include Bank of America, HSBC, Intel, and Microsoft. It supports tools automating business logic across company boundaries. Corda has become a popular choice in the insurance industry for streamlining claims processing, closing, and settlement.
5. Tezos
Developed since 2014, Tezos supports dApps, smart contracts, and financial instruments, such as NFTs. The platform supports upgradable protocols and modular software clients, allowing it to adapt to new uses. It uses a PoS consensus mechanism. An on-chain upgrade mechanism allows developers to add new features without creating a new blockchain, which requires migrating users. The Tezos community has regularly enhanced the platform with improvements in performance and increased the size limit on smart contracts. The Oxford 2 protocol, a recent update, improved the PoS mechanism, a new version of Timelocks encryption to improve security, and private smart rollups, which enable permissioned and permissionless deployments.
6. EOSIO
Launched in 2018, EOSIO is optimized for developing dApps and smart contracts and features a PoS-based consensus mechanism. The platform also includes governance features for voting on changes. Strong points include fast transactions and account permission features for deploying applications. More than 400 applications have been developed on the platform, and the community provides tools for customizing blockchain implementations. EOSIO-Taurus, designed for enterprise performance on private blockchains, includes secure, high-volume transactions with features such as automatic failover and disaster recovery. A more recent hard fork in September 2024 activated a new consensus algorithm called Savanna, which is dramatically faster, more scalable, and more secure.
7. Stellar
Stellar is a newer blockchain platform optimized for DeFi applications using the Stellar Consensus Protocol. It features security mechanisms for eliminating problematic actors in a financial transaction. It has been adopted for international trade and cross-border money transfers. Examples of applications on the Stellar blockchain include MoneyGram, Circle, and Flutterwave. The Soroban smart contract platform streamlines the development of Web 3.0 and DeFi applications.
8. Consensys Quorum
Quorum is a customized version of Ethereum developed by JPMorgan Chase, optimized for high-speed transactions between institutions on a private network. Consensys partnered with Visa and Mastercard to improve services. Quorum also adds various privacy enhancements to Ethereum to improve support for regulations such as GDPR. Consensys acquired the Quorum platform from JPMorgan Chase in late 2021 and integrated it into its own work to create the Consensys Quorum open source protocol layer. The firm provides development services to enterprise customers. In 2022, it launched Quorum Blockchain Service on Microsoft Azure. The company has developed an extensive ecosystem of supporting tools and services to enhance Quorum’s value.
George Lawton is a journalist based in London with extensive experience covering technology.


