Recently, the phrase ‘You can’t lick a badger twice’ went viral on social media, becoming a symbol of Google’s AI Overviews ability to generate plausible explanations for made-up idioms. When users type a random phrase into Google followed by ‘meaning,’ the AI Overview provides a confident interpretation, often with surprising results. For instance, Google interprets ‘you can’t lick a badger twice’ as a warning against deceiving someone more than once, linking ‘lick’ to ‘trick or deceive’ and badger to historical badger baiting. Other examples include interpreting ‘dream makes the steam’ as a statement about imagination powering innovation and ‘you can’t humble a tortoise’ as a comment on the difficulty of intimidating someone with a strong character. While the AI’s confident tone can be off-putting, particularly when it hallucinates sources, its attempts to derive meaning from gibberish are often impressive and sometimes poetic. For example, when asked about ‘two cats are better than grapes,’ the AI correctly notes that grapes can be toxic to cats. However, the technology’s tendency to present guesses as facts can be misleading. In one notable exception, Google’s AI Overview expressed uncertainty when interpreting ‘when you see a tortoise, spin in a circle,’ acknowledging it wasn’t a standard expression and offering possible connections to Japanese nursery rhymes. The article highlights both the capabilities and limitations of Google’s AI Overviews in handling nonsensical input, demonstrating its potential for creative interpretation while cautioning against over-reliance on its factual accuracy.
Examples of Google’s AI Interpretations
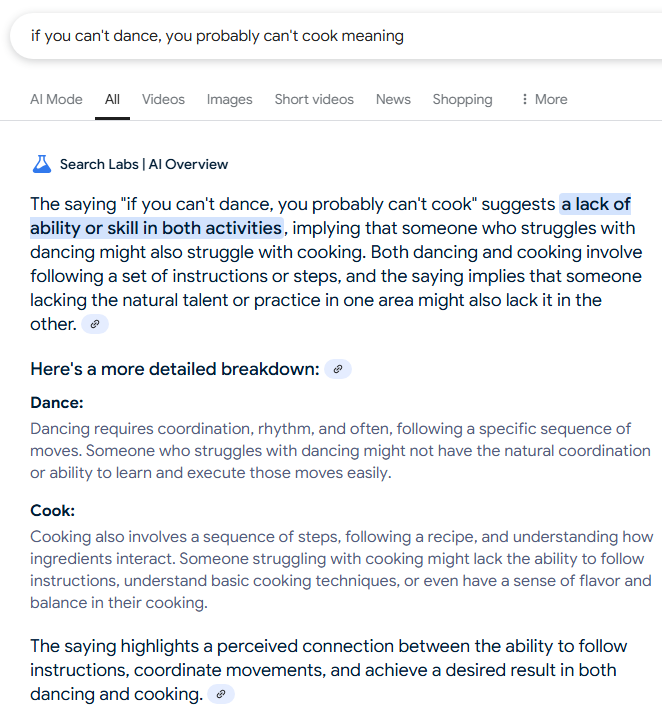
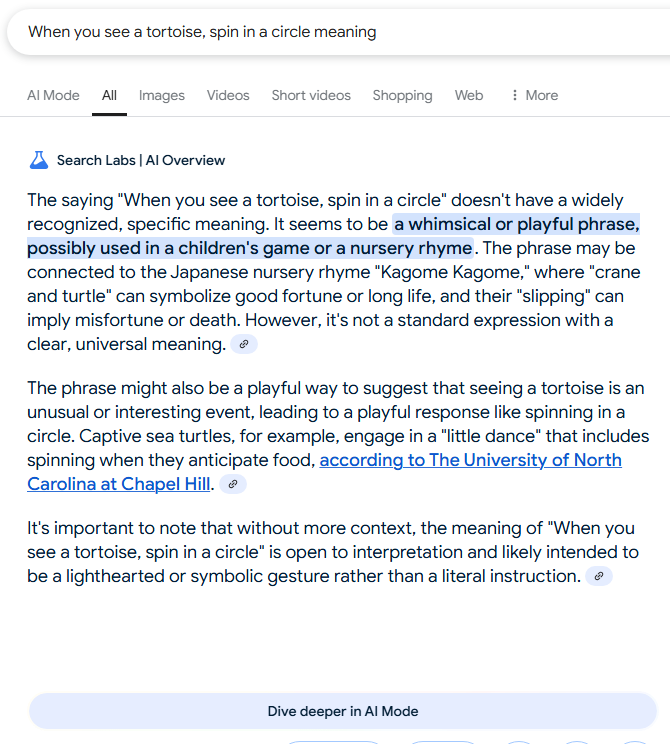
The AI’s interpretations range from plausible to hallucinatory, sometimes creating connections that weren’t intended by the original phrase creators. While users often express horror or amusement at the AI’s takes on their made-up idioms, the technology demonstrates a remarkable ability to force meaning from nonsense. However, the persistent problem of LLMs making up sources and presenting them as facts remains a significant concern. As with any AI-generated content, users must remain cautious about trusting the information presented.
Conclusion
Google’s AI Overviews represent a significant advancement in natural language processing, capable of generating creative and sometimes insightful interpretations of even the most nonsensical phrases. While the technology is not without its flaws, particularly regarding factual accuracy and source reliability, it offers a fascinating glimpse into the potential of AI to understand and generate human-like language. As AI continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how such technologies balance creativity with factual accuracy in the future.


