Patient compliance with medication is a persistent challenge in achieving the best treatment outcomes. Traditional methods often struggle to ensure patients consistently take their prescribed medications. However, innovation, especially in the realm of remote medication management, is offering new solutions.
MIT World Peace University (MIT-WPU) in Pune has developed a modular, Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled tablet and capsule dispenser designed to automate and remotely monitor medication management. This device aims to address the difficulties of complex dosing schedules. This innovation is a notable contribution to India’s continuing med tech revolution.

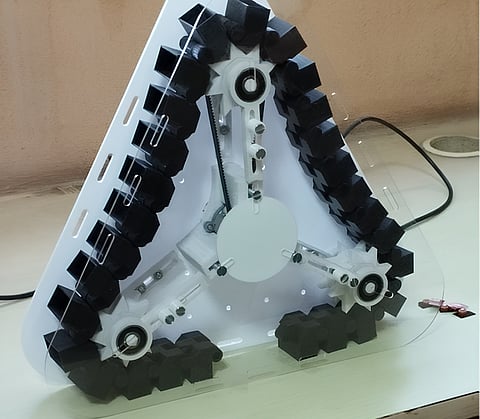
The device features an equilateral-shaped container, a motor-driven dispensing system, and a controller unit. This allows users to define dispensing schedules and enables real-time remote monitoring. According to the researchers, the dispenser integrates advanced IoT connectivity with a modular design. This allows caregivers and healthcare professionals to monitor medication adherence remotely.
“In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining consistent medication adherence is a major challenge, especially for individuals managing complex medical regimens. This innovative IoT-enabled pill dispenser represents a major step forward in addressing this issue,” says Dr. Amol Tagalpallewar, Professor at the School of Pharmacy at MIT-WPU. He further states that the technology improves health literacy and quality of life.
The dispenser uses dispensing units arranged circumferentially, connected by sprockets and powered by a motor. The controller unit sends command signals at user-specified times, leading to automated dispensing. The IoT integration enables real-time monitoring, which can improve patient safety and care.
Dr. C. H. Patil, Associate Professor at the School of Computer Science and Engineering at MIT-WPU, envisions a future where technology and human-centered design create more accessible, efficient, and effective solutions. The ongoing rise in chronic illnesses combined with an aging population needing consistent medical care makes this innovation particularly significant for use in assisted living, home care, and hospital settings.
While the technology shows promise, the researchers haven’t yet released details concerning commercialization plans, technology licensing, manufacturing, scalability, or cost. The technology’s accessibility and ultimate utility will depend on industry advancements and movement to the end user.