This article reflects insights from Microsoft Digital, originally published in 2018, detailing the company’s internal use of Microsoft 365 to boost employee productivity and foster better teamwork.
The Evolution of Collaboration at Microsoft
Microsoft has embraced Microsoft 365 tools, including SharePoint Online, Microsoft Teams, Exchange Online, and Viva Engage, to support modern work styles and drive digital transformation. Microsoft is also integrating the modules of Microsoft Viva with its Microsoft 365 products. The platform provides a central hub for employees to access the latest project updates, files, and data, which helps to empower teams and enable the organization to adapt quickly to shifting business needs.
Adapting to a Changing Collaboration Landscape
The way people collaborate is ever-changing. Today’s workers frequently collaborate with more people, more often, and in dynamic, hybrid, or remote arrangements. This environment has led to several key shifts:
- Workers are participating in twice as many collaborative teams as they were five years ago.
- The average information worker has seen the time spent on their day-to-day tasks increase by 50 percent.
- Companies investing in teamwork and collaboration are significantly more likely to perform well.
The Changing Face of Collaboration
Collaboration now extends beyond the boundaries of the internal organization, requiring tools that support external interactions while protecting data and users. Microsoft employees can seamlessly collaborate with any external user in a secure and scalable way. Teams are also increasingly globally distributed, needing tools for connecting across locations and time zones. Asynchronous work has become more common in this landscape, particularly in hybrid work environments, as employees need to balance their schedules with the demands of staying connected.
From Workplace to Workspace
One of the most significant changes is the way and place where work is done. In the past, the pace of business was generally slower. In the past, data was kept on-premises, computers were primarily used at work and decisions were made within set business hours. Now, the situation is different and accelerated by technology. The arrival of millennials in the workforce, the first digital natives, has also changed worker expectations regarding connectivity and work styles:
- There is now an expectation around pervasive connectivity.
- Work is no longer linear.
- Technology has streamlined processes, allowing for more time to improve the employee experience, and workers have access to tools to improve their productivity.
- It is easier for employees to move from project to project and for organizations to use talent on demand.
Microsoft’s culture now focuses on employee experience and uses teamwork to achieve common goals. Employees want to access their workspace anytime and anywhere. They are connected, networking, and collaborating constantly, and the company rewards results more than office hours.
Driving Internal Collaboration
Microsoft constantly evaluates collaboration patterns to optimize service and tools. By understanding how teams work, the company can provide them with the right collaborative toolset and mindset.
Collaboration at Microsoft is about culture and technology. Teams establish their own collaboration standards, and Microsoft asks important team-related questions, such as team composition, work nature, team duration, and the location of team members. This enables them to determine which practices and tools work best based on their existing ecosystem.
Enabling Collaboration with Microsoft 365
Productivity involves creating flexibility that meets the needs of employees, in line with the company’s mission to empower everyone. Microsoft 365 is a central technology in Microsoft’s collaborative landscape, providing a unified environment with a centralized framework, identity management solution, and first-class security standards. This unified environment allows for easy sharing and collaboration, ensuring that all employees are in sync.

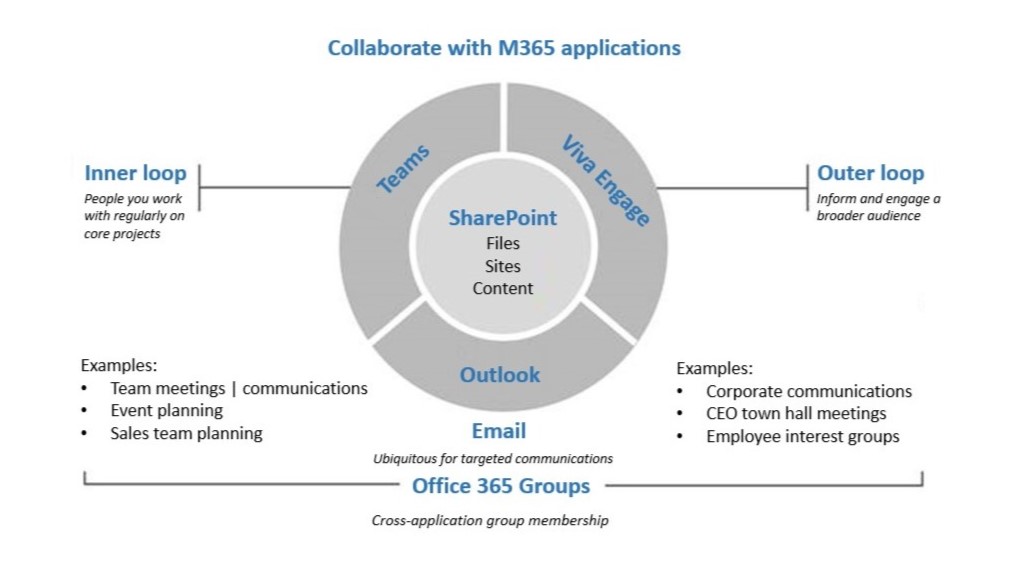
Different Apps, Different Collaboration Types
Microsoft uses each purpose-built application in the Microsoft 365 suite to drive different aspects of collaboration and teamwork:
- Microsoft Teams: Acts as the hub for active groups working on projects.
- SharePoint: Serves as the content center for files, news, and pages, both internally and externally.
- Outlook and Exchange Online: Enables communication.
- Viva Engage: Connects people across the company.
Microsoft 365 empowers both synchronous and asynchronous collaboration, allowing teams to build on each other’s work. Teams offers meeting recordings, AI-generated summaries, and document co-authoring within a comprehensive ecosystem.
Teams as the Hub for Teamwork
Microsoft Teams has revolutionized hybrid collaboration within the Microsoft 365 universal toolkit. Teams, as the central hub, meets the communication needs of a diverse workforce while consolidating information.
Microsoft Teams brings together conversations, notes, meetings, and files. Extensible features like tabs and apps allow integration with other systems. In a practical application, support teams at Microsoft handle support incidents within Teams, using real-time dashboards and integrated alerts. Due to companywide familiarity with Teams, these functions are easy to use and set up, which leads to faster incident resolution.
Teams integrates with the other apps used by employees, such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, OneNote, SharePoint, Planner, Stream, and Power BI. This facilitates seamless management of communications, which can then be easily published in Viva Engage communities for broader engagement. With the adaptable platform, development teams can customize their workspaces with features such as tabs, connectors, and bots to suit the specific needs of their teams and tasks. It provides a complete meeting room experience, where teams can chat, share content, and use audio and video conferencing. Channel meetings support broad information sharing.
Sharing Information with SharePoint and OneDrive
SharePoint and OneDrive for Business are the core for file storage, and sharing needs.

Sharing Documents
Using SharePoint for Team Collaboration
SharePoint is the primary repository for file and data storage for all collaborative needs within Microsoft.
- Data, processes, and files containing corporate information, belonging to projects or teams, and anything shared internally is stored in SharePoint and OneDrive for Business.
- Microsoft 365 groups are the primary tool for managing access in SharePoint.
- Check-in workflows can be created to assign a document to the next person in line when a reviewer checks it in.
- Permissions are granted on a site basis, with options to uniquely share or restrict individual documents.
SharePoint offers teams several advantages, including cloud-based storage for security, continuity, and accessibility. Sites and content are discoverable through search, with team-specific metadata for better results. SharePoint also has policies and governance in place and allows lifecycle management, control over permissions, and version histories.
SharePoint also hosts all of Microsoft’s internal sites, including its company intranet homepage (MSW), which offers company news, important announcements and events, and internal resources and tools.
Protecting Files with the Cloud
Because working with files saved to personal devices can create security concerns, Microsoft encourages use of OneDrive for Business, its individual file library for storing personal work or files that don’t require external sharing. OneDrive for Business safely stores files in the cloud by default, and are private unless shared intentionally or placed in a shared folder. It’s made it easy to access and sync files from any device. OneDrive for Business is a solid solution for collaboration, even if scope is limited.
From an IT perspective, there are several advantages to using OneDrive for Business:
- Files aren’t stored on a user’s hard drive.
- Cloud storage is more secure, has continuity, and it’s accessible to employees even when their primary device is not.
- Employees can recover their files or revert to a previous version.
- It’s discoverable for the people it’s shared with.
- Policies and governance can be applied.
Collaborating and Connecting with Viva Engage
Viva Engage is Microsoft’s social network that supports broad, and online community and connection. Individuals can share information, ask questions, and discuss topics through community forums or through personal storylines. Leaders can share announcements with employees throughout Microsoft. Viva Engage also provides a platform for Q&A during live events, which enables employees to interact with leadership.
Microsoft Graph and Intelligence
Microsoft has a unified, suite-wide intelligence with Microsoft Graph that maps the connection of people and content to surface insights. Examples of this include features such as email address autocomplete in Outlook and content guidance in SharePoint Home, and the recent documents shown on one device are the same as those shown on another device.
Enabling Cultural Change
While the decision to implement a change such as Microsoft 365 adoption may originate at the organizational or executive level, the changes are typically based on the evolving business needs of the Microsoft organization and its people. Microsoft’s employees are encouraged to support their peers and build from each other’s work and are rewarded when they do. With Microsoft 365, employees can work seamlessly, securely, and feel connected. Microsoft uses four pillars of change management: Awareness, Engagement, Measurement, and Management.

Enabling Behavior and Change for Better Collaboration
With Microsoft 365, a shift in behavior represents a new way of working. Microsoft has established behavior adjustments, including the use of groups instead of distribution lists, chat over email, cloud usage, and mobile work.
Managing Compliance and Security
Because Microsoft 365 hosts the entire collaboration environment, security and data protection are of great importance. The company relies on its identity and access strategy, which governs all processes and tools used throughout the identity lifecycle for employees, partners, and suppliers. Microsoft uses Microsoft Entra Connect and multi-factor authentication to ensure data safety, and is able to support a number of identity models.
Conclusion
Enterprise collaboration is centered on cultural change and empowering employees to work together. Microsoft is transitioning from a competitive environment to one of teamwork, through tools such as Microsoft 365, and encourages communication between leaders and employees and shared team workspaces. Making the company’s global workforce more productive is also key, with unified communication through Teams chat and Viva Engage.
Microsoft continues to use Microsoft 365 to improve teamwork and collaboration by providing a unified framework to achieve business goals, support changing workstyles, and enable continued digital transformation.