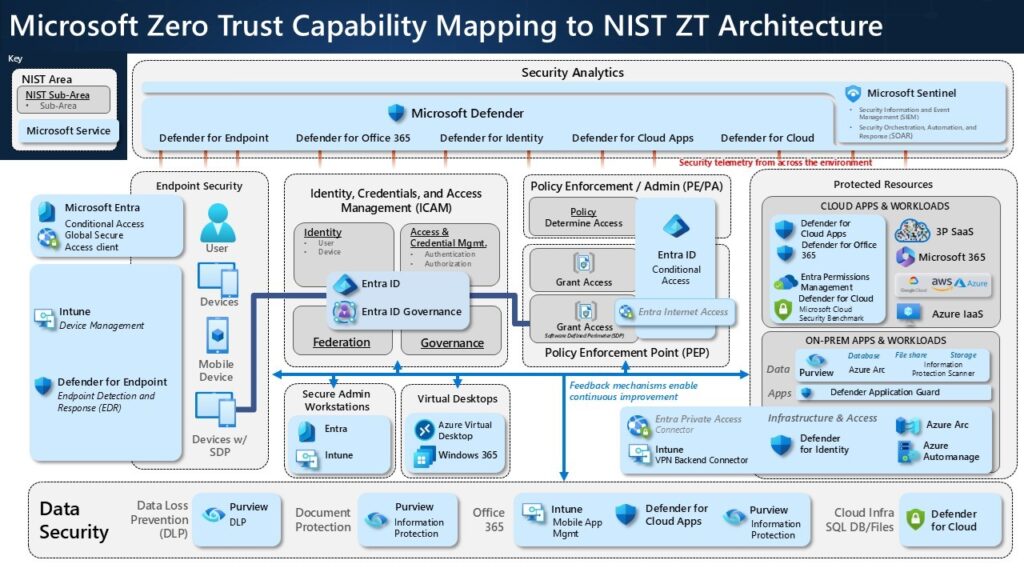
Microsoft and NIST Release Practical Guide for Zero Trust Implementation
Microsoft, in collaboration with the National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence (NCCoE), has announced the release of a new practice guide detailing how organizations can implement a Zero Trust security strategy. This guide offers practical steps and insight into the end-to-end security approach enabled by Zero Trust principles.
The Zero Trust model, gaining significant momentum in the cybersecurity landscape, often leaves customers seeking clear guidance on effective deployment using available technologies. To address this, Microsoft joined an ongoing collaboration led by the NCCoE, a part of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). This effort aims to provide customers with valuable references for Zero Trust implementations.
Since 2022, the NCCoE has worked with 24 vendors, including Microsoft, to develop this practice guide. The guide outlines practical steps that organizations eager to adopt Zero Trust can follow to implement cybersecurity reference designs.
Core Principles of Zero Trust
Zero Trust is built on the following core principles:
- Assume Compromise: Operate under the assumption that a breach is inevitable, driving a proactive, holistic security approach.
- Explicit Verification: Verify trust explicitly before granting access to assets, ensuring only authorized users and devices have access.
- Least Privilege: Limit the blast radius by granting only the minimum necessary privileges.
The Zero Trust model offers a collaborative and comprehensive approach to end-to-end security, crucial for adapting to the ever-changing landscape of threats, technologies, and business needs.
“The NCCoE strives to launch initiatives that directly benefit organizations facing modern cybersecurity challenges. The lessons learned from integrating various products and services contributed by collaborators like Microsoft is an invaluable contribution toward this effort.” —Alper Kerman of NIST
NIST’s Role in Cybersecurity
NIST, a long-standing authority in cybersecurity, has published security standards for decades, and its NCCoE has been instrumental in clarifying how to design and implement Zero Trust. The NCCoE achieves this by publishing how-to guides, practice guides, and business case examples.
“The NCCoE is dedicated to helping organizations strengthen their cybersecurity. A major way we do this is by translating existing security standards into example implementation guidance, so organizations know exactly what they need to do to protect their most critical assets. By simplifying the process, we can get more organizations benefiting from Zero Trust principles.” —Alper Kerman of NIST
Microsoft and the NCCoE: A Collaborative Approach
Microsoft has a history of engagement with NIST’s open standards development processes, specifically supporting the NCCoE’s mission to develop practical cybersecurity approaches. These approaches demonstrate how the components of Zero Trust architectures can securely mitigate risks and meet industry compliance requirements.
When the NCCoE sought industry partners in October 2020 to support the Zero Trust architecture project, Microsoft readily joined the initiative. This project, one of the most extensive undertaken by the NCCoE, involved 24 participating organizations, seventeen different builds, and a wealth of practical documentation.
The goal of the NCCoE project is to showcase several example Zero Trust architecture solutions that can be applied to a conventional enterprise IT infrastructure. These solutions are designed and deployed according to the concepts and tenets outlined in NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-207, Zero Trust Architecture. These documents effectively demonstrate how to implement Zero Trust principles using today’s technology. The project addresses several common scenarios organizations may face, including:
- Employees seeking access to corporate resources.
- Employees accessing internet resources from enterprise devices.
- Contractors attempting to access corporate and internet resources.
- Communication between servers within an enterprise.
- Secure collaboration with business partners.
- Integrating monitoring and SIEM systems with the policy engine.
As a result of this effort, the Zero Trust Architecture 1800-35 practice guide is now available. The guide details a standards-based implementation of Zero Trust architecture and provides use cases, various example implementations, and documentation to enhance understanding.

The Future of Zero Trust
Both Microsoft and NIST are exploring ways to leverage this foundational work to support additional use cases and ensure a more secure digital environment. Microsoft is closely monitoring the U.S. Executive Order 14028 on Cybersecurity and the OMB Implementation Strategy, which emphasizes Zero Trust architecture. The company is continuously improving its offerings to help customers address their evolving security challenges.
The integration of AI and its close relationship to Zero Trust makes securing data and AI implementations increasingly urgent; a network perimeter alone is no longer sufficient.
Microsoft is working to ease these challenges through NIST’s NCCoE Zero Trust Architecture consortium, with its Security Adoption Framework (SAF), The Open Group Zero Trust Standards, and other security guidance.
About the National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence
The NCCoE, part of NIST, is a collaborative hub where industry organizations, government agencies, and academic institutions work together to tackle pressing cybersecurity challenges. This partnership fosters the creation of practical cybersecurity solutions for diverse industries and cross-sector technology challenges. The NCCoE develops modular, adaptable cybersecurity solutions using commercially available technologies and documents these efforts to deliver practical guidance for organizations of all types.
Information is available at https://www.nccoe.nist.gov.