Advances in Quantum Sensors: Transforming Healthcare
The 2025 International Year of Quantum Science and Technology highlights the exciting applications of quantum physics in various fields, including medicine and healthcare. Quantum sensors, in particular, are poised to revolutionize the way we study the human body and diagnose diseases. Several quantum-based systems are nearing commercialization, promising significant improvements in medical diagnosis and treatment.
The Importance of Quantum Science in Healthcare
The connection between quantum science and healthcare is not new. In 2013, academics and government representatives identified healthcare as a primary application for quantum technologies when planning the UK’s National Quantum Technologies Programme. This £1bn initiative, recently renewed for another decade, continues to prioritize healthcare. Most major hospitals already utilize quantum sensors in the form of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, which manipulate the quantum spin states of hydrogen atoms to image soft tissues.
New Generation of Nanoscale Quantum Sensors
Recent advancements have led to the development of nanoscale quantum sensors capable of detecting magnetic fields emitted by biological systems. These sensors, often consisting of a single atom or using photons, electrons, or spin defects in materials like diamond, offer unprecedented sensitivity. Companies such as Element Six and Quantum Total Analysis Systems (QTAS) are at the forefront of this technology, developing devices that can quickly identify biomarkers in bodily fluids.
Five Promising Areas for Quantum Sensors in Healthcare
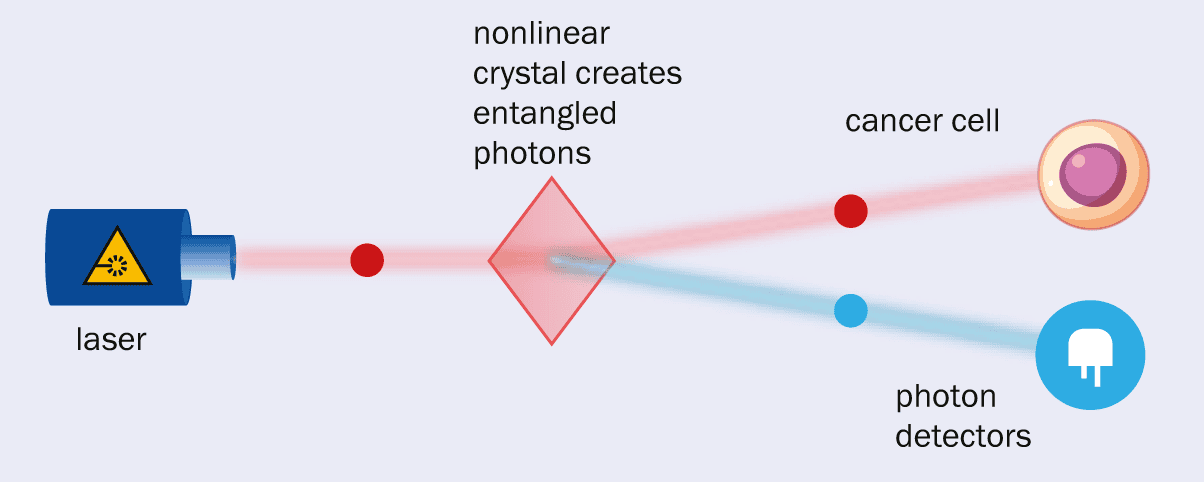
- Lab Diagnostics: Quantum sensors can help identify diseases like cancer by monitoring internal body changes. For instance, Digistain’s EntangleCam uses entangled photons to detect cancer cells without damaging samples.
- Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Quantum technology can miniaturize and improve the accuracy of diagnostic tests, making them suitable for use in hospitals, clinics, or even at home. Companies like Element Six are developing diamond-based devices to detect specific proteins and diagnose diseases early.
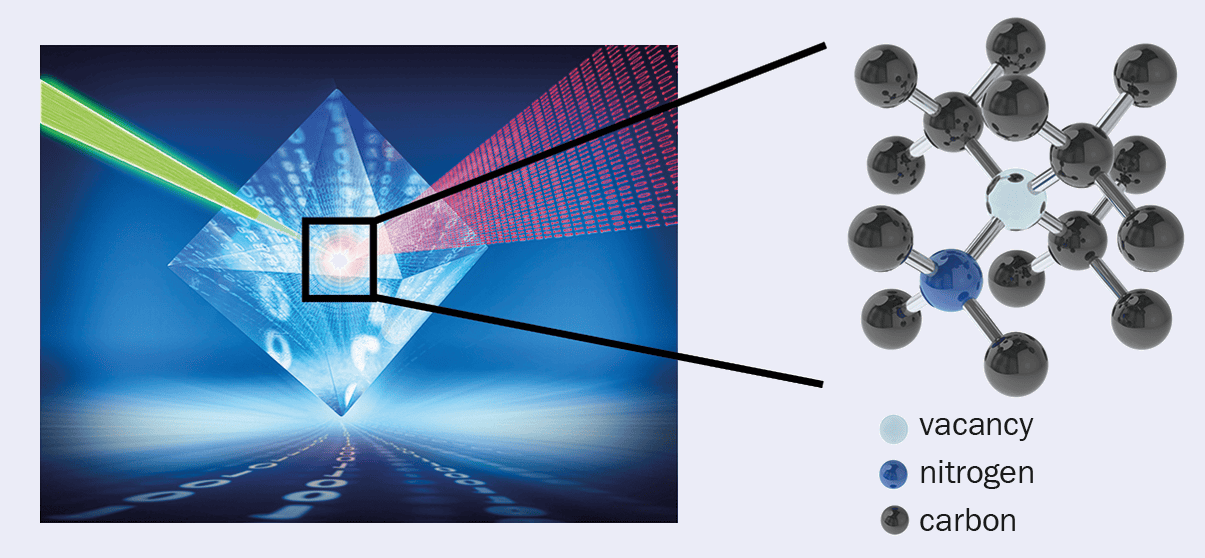
-
Consumer Medical Monitoring and Wearable Healthcare: Devices like NIQS Tech’s glucose sensor use quantum interference effects to provide accurate, non-invasive health monitoring.
-
Body Imaging: Quantum-based scanning techniques, such as those developed by Cerca Magnetics and Kromek, are improving diagnostic imaging. Kromek’s cadmium zinc telluride semiconductors, for example, enable ultralow-dose molecular breast imaging.
- Microscopy: Quantum technologies are enhancing microscopy techniques, such as ghost imaging using entangled photons, to improve sample imaging and analysis.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising advancements, significant challenges remain before quantum sensors can be widely adopted in clinical settings. Scalability and reliability are key concerns. However, the field is rapidly evolving, with new companies emerging to address these challenges. The UK’s quantum hubs, such as Q-BIOMED and QuSIT, are playing a crucial role in bringing academia and industry together to commercialize quantum sensor technologies.
As quantum sensors continue to mature, we can expect significant improvements in healthcare diagnostics and treatment. The next five years will be critical in determining the impact of these technologies on the medical field.