The medical device industry is rapidly evolving with innovations ranging from implants and wearables to complex combination products. Regulatory agencies worldwide have established expedited pathways to bring these technologies to patients more efficiently. This review examines the regulatory landscape of accelerated approval pathways for medical devices in the United States and European Union.
United States Regulatory Framework
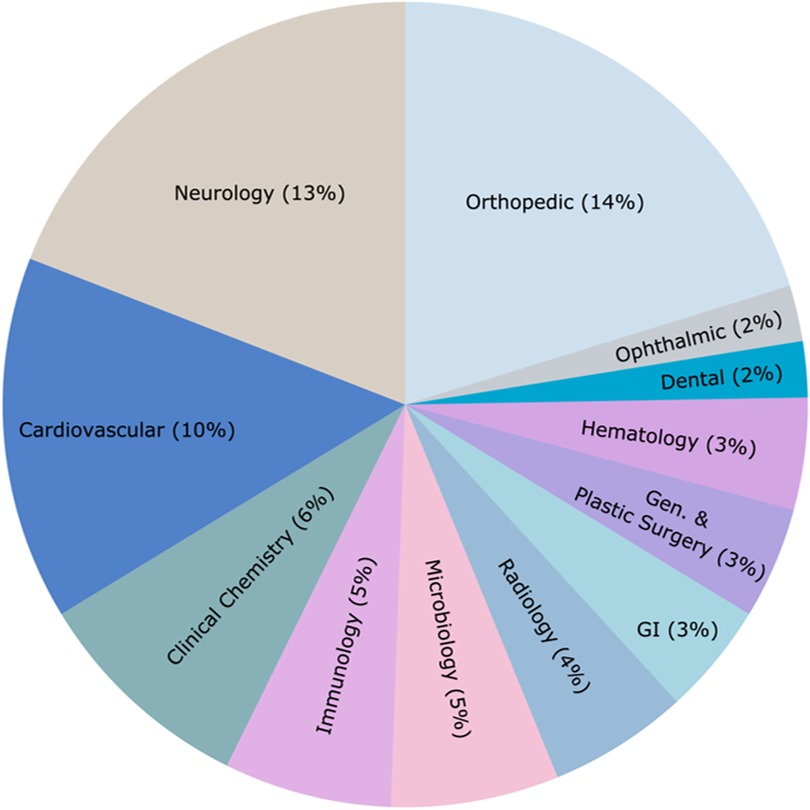
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) introduced the Breakthrough Devices Program (BDP) in 2015 to accelerate the development and review of innovative medical devices. The program aims to provide more effective treatment or diagnosis of life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating diseases. As of September 2024, 12.3% of 1,041 BDP-designated devices received marketing authorization. The mean decision times for BDP-approved devices were significantly faster than standard approvals.
European Union Regulatory Framework
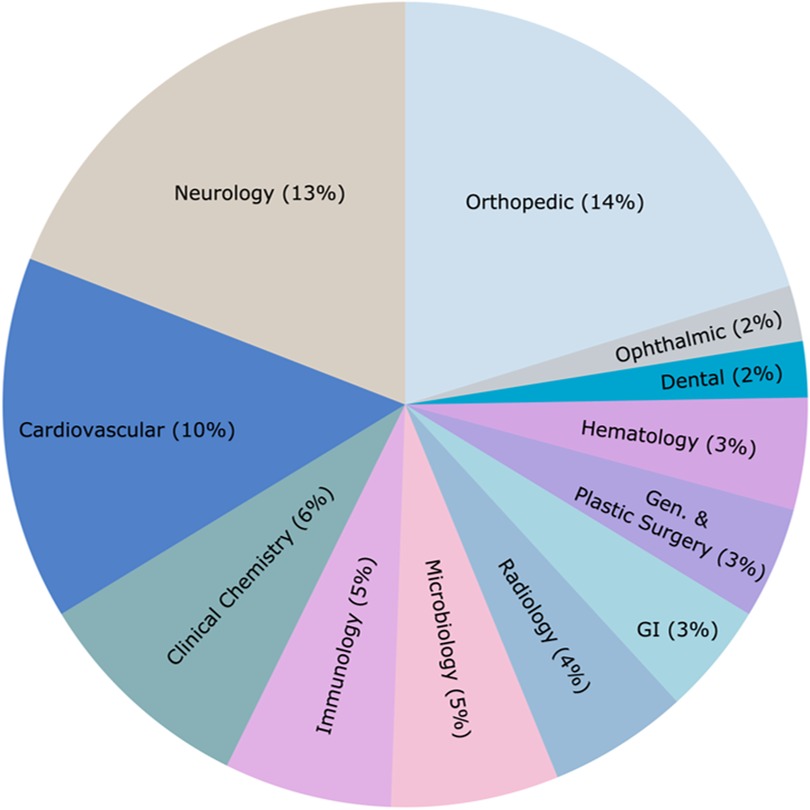
The European Union has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and Health Technology Assessment Regulation (HTAR) to streamline the approval process. The HTAR introduces joint clinical assessments and scientific consultations to reduce duplication of efforts across member states. While there’s no specific accelerated approval pathway, these regulations aim to harmonize approval processes.
Funding and Coverage Mechanisms
Both the US and EU have implemented various funding and coverage mechanisms to support innovative medical devices. In the US, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has introduced initiatives like the Transitional Coverage for Emerging Technologies (TCET) pathway. In the EU, countries like France, Germany, and Belgium have established programs such as Prise en Charge Transitoire (PECT), Innovation Funding (IF), and Digital Health Applications (DiGA) to facilitate early access to innovative technologies.
Challenges and Recommendations
While accelerated pathways expedite market entry, they also introduce challenges in balancing rapid access with safety considerations. Robust post-market surveillance and real-world evidence collection are crucial. Global convergence efforts, including harmonized standards and mutual recognition agreements, can streamline regulatory processes. Regulatory authorities must maintain independent decision-making capabilities while adopting convergent practices.
The successful implementation of accelerated approval pathways requires ongoing evaluation and adaptation to ensure they meet their intended goals without compromising patient safety or healthcare system sustainability. Collaboration between regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, and healthcare systems is essential to refine these pathways and develop standardized approaches to evidence generation and post-market surveillance.