The Dark Side of Blockchain: Examining the Impact of Blockchain Technology Adoption on Corporate Default Risk
Blockchain technology has rapidly integrated into the digital landscape, influencing new infrastructure and various sectors, including 5G technology, artificial intelligence, and digital finance. With increasing attention from the capital market, the adoption of blockchain technology has significant financial implications for the stock market. Studies have shown positive responses to 8-K disclosures related to blockchain technology by U.S. listed companies (Cheng et al., 2019) and that blockchain technology is a highly marketable type of fintech patent (Chen et al., 2019). The upward trend in blockchain technology adoption disclosures since 2009 suggests its pervasive integration.
However, despite its potential, blockchain technology is considered immature by many, leading to corporate violations and legal issues. For example, Playboy Enterprises filed a lawsuit against Global Blockchain Technology for failing to integrate the technology into Playboy’s online media channels (Los Angeles Times, August 2018). Similar issues have emerged in China, where the hype around blockchain technology led to regulatory crackdowns on companies attempting to exploit the trend (Shenzhen Stock Exchange, January 16, 2018). This raises the question of whether blockchain technology adoption truly increases market value or is simply another form of market hype (Autore et al., 2024).
One perspective, the Technology Acceleration Perspective, views blockchain as a tool to improve data processing efficiency (Chen et al., 2019; Cheng et al., 2019; Xu and Zou, 2021). By enhancing financial activities like mutual funds and supply chain finance, blockchain technology can increase value in the financial market (Beck et al., 2010). The large number of nodes easily attracts users, potentially leading to a higher market value of a company disclosing blockchain adoption.
Conversely, the Managerial Opportunism Perspective suggests that managers might use technology strategically to mislead investors through misinformation and price manipulation (Cheng et al., 2019; Cahill et al., 2020). Cioroianu et al. (2021) found that blockchain information disclosure increases contagion risk, while Autore et al. (2024) discuss that market misperceptions regarding blockchain could lead to firms managing their earnings upward. This study investigates whether blockchain technology increases or decreases corporate default rates and explores the underlying mechanisms.
Research Questions and Methodology
Our research investigates two key questions:
- Does blockchain technology increase or decrease the corporate default rate?
- What are the possible mechanisms?
To address these questions, the expected default model (Bharath and Shumway, 2008) was employed to measure default probability. The study examines the relationship between blockchain technology adoption and corporate default risk within the Chinese market. The timeframe is from 2001 to 2021.
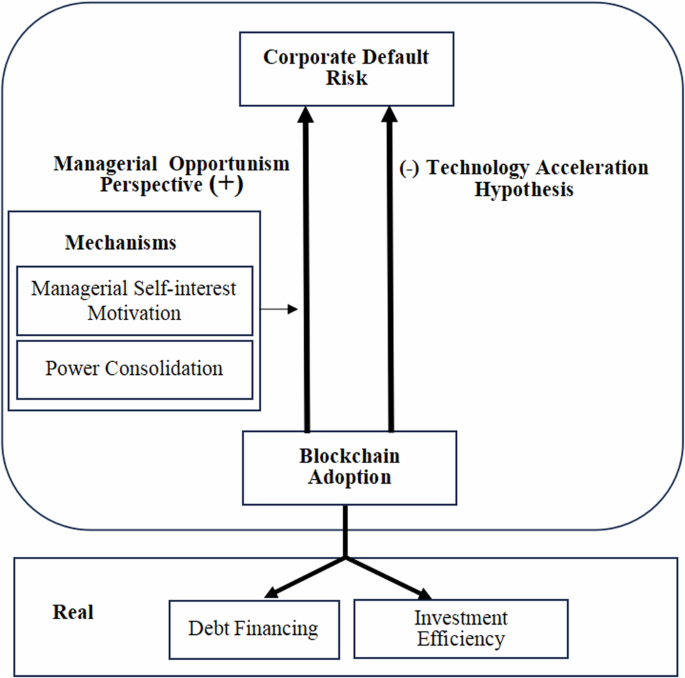
Image 1: Block Chain Technology Adoption and Corporate Default Risk Framework
Image 2: Placebo Tests
Core Findings
The results suggest that the adoption of blockchain technology can increase the probability of corporate default, which points to potential managerial opportunism. The study reveals that managers may use blockchain technology to mask self-interested activities, which is linked to lower-quality earnings and less investment efficiency. Robustness checks, including instrumental variable tests, DID tests, and endogenous tests, support these findings.
The research points to two key mechanisms:
- CEO short-termism: This focuses on the tendency for executives to prioritize short-term gains over the long-term health of the company.
- Power Consolidation: This is linked to the tendency of managers to utilize blockchain technology to achieve personal gains.
Key contributions
This research adds to the understanding of the negative impacts of blockchain adoption (Cioroianu et al., 2021; Griffins and Shams, 2020; Gandal et al., 2018). The study shows that blockchain technology can harm companies when it is misused. Managers may view it as a source of financing, thus concealing their true performance and increasing the risk of default.
Institutional Background and Hypothesis
The study investigated the application of blockchain technology in financial services, which has been praised for bringing transparency, time efficiency, and productivity to the financial sector. The adoption of blockchain technology helps to reduce the chances of data breaches and operational risks.
Hypothesis Development
Two major hypotheses relate to the adoption of blockchain technology and corporate default risks: the technology acceleration hypothesis and the managerial opportunism perspective.
- Technology Acceleration Hypothesis: blockchain adoption could reduce the corporate default rate.
- Managerial Opportunism Perspective: Blockchain adoption could increase the corporate default rate.
Policy Implications
The government must take measures to guide and regulate blockchain technology implementation in businesses, establishing regulations to promote the reasonable usage of blockchain for real economic development.