What is Digital Health?
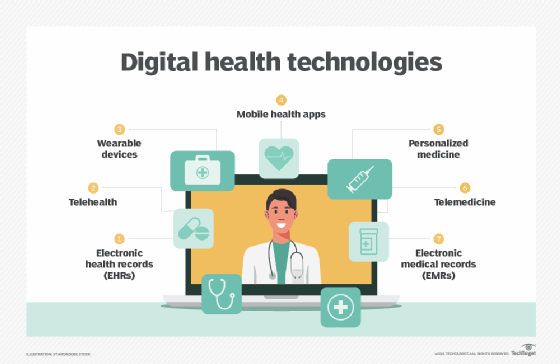
Digital health, also known as digital healthcare, refers to the use of digital technologies in healthcare. This broad term encompasses various categories of technology, including mobile health (mHealth) apps, electronic health records (EHRs), electronic medical records (EMRs), wearable devices, telehealth and telemedicine, and personalized medicine. By incorporating software, hardware, networking, and sensors into healthcare delivery systems, digital health has revolutionized the field, generating numerous benefits for both caregivers and patients.
Key Components of Digital Health
- Wearable devices
- Mobile apps
- Telehealth and telemedicine
- Diagnostics tools
- Predictive modeling
- Patient portals
- Decision support systems
- Digitized health record platforms
- Bioinformatics tools
These digital health tools incorporate various technologies to deliver more advanced capabilities, improve efficiency and accuracy, and reduce errors. Key technologies include:
- Automation
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data
- Robotics
Applications of Digital Health Technologies
- AI in Healthcare: AI quickly identifies patterns in vast amounts of data, aiding in diagnostics, clinical documentation, risk factor identification, and personalized treatment plans.
- Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Network-connected medical devices that enhance care quality and safety, such as ingestible sensors and remote patient monitoring devices.
- mHealth: Includes wearables, mobile apps, and devices supporting care delivery, patient monitoring, and chronic disease management.
- Blockchain-based EMRs: Emerging technology enhancing patient data integrity and interoperability.
- Augmented Reality (AR) in Healthcare: Creates immersive environments for patient experience enhancement, surgical planning, and simulation-based training.
Benefits of Digital Health
Digital health innovations help healthcare organizations save time and money while improving accuracy, efficiency, and profitability. They achieve this by combining medicine with numerous technologies and technology-enabled innovations. Patients can use digital health technologies to manage their health, access medical history, communicate with providers, and make informed decisions.
Challenges in Digital Health
Despite its benefits, digital health faces several challenges:
- Data Interoperability: Difficulty in using data meaningfully due to different storage and coding systems.
- Digital Literacy: Patients’ lack of digital literacy hinders effective use of available tools.
- Data Security and Privacy: Concerns regarding data storage, access, sharing, and ownership.
- Ethical and Insurance Issues: Questions around responsibility in cases of medical errors with robotic assistance.
The Future of Digital Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digital transformation in healthcare, with technologies like telehealth platforms and remote patient monitoring becoming more prevalent. The global digital health market is expected to grow significantly, driven by aging populations, increasing healthcare costs, and government initiatives supporting digital health.